GENITAL HERPES
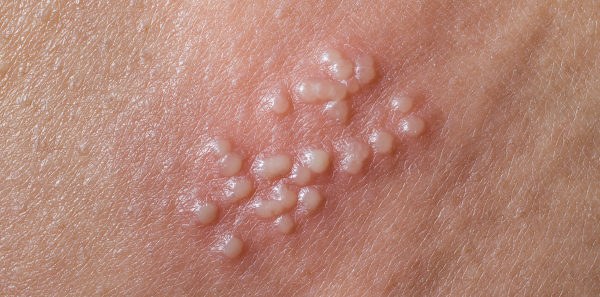
What is Genital Herpes?
Genital herpes is an infection of the genitals, buttocks, or anal area caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV). Most genital herpes is caused by HSV type 2. Yet as people begin to have sex at younger ages the herpes type 1 virus has increasingly been shown to also cause genital herpes. [1]
How Common is Herpes?
Results of a nationally representative study show that in the USA 16.2%, or about one out of six, people 14 to 49 years of age have genital HSV-2 infection. [2] Over the past decade the percentage of Americans with genital herpes in the U.S. has remained near this value. Genital HSV-2 infection is more common in women (approximately one out of five women 14 to 49 years of age) than in men (about one out of nine men 14 to 49 years of age). [2] Transmission from an infected male to his female partner is more likely due to the location of the virus.
How do you get Herpes?
HSV-1 and HSV-2 can be found in and released from the sores that the viruses causes but they also are released between outbreaks. Generally, a person can only get HSV-2 infection during sexual contact with someone who has a genital HSV-2 infection. [2] Transmission can occur from an infected partner who may not know that he or she is infected.
HSV-1 more commonly causes infections of the mouth and lips. HSV-1 infection of the genitals can be caused by oral-genital or genital-genital contact with a person who has HSV-1 infection. Genital HSV-1 outbreaks recur less regularly than genital HSV-2 outbreaks. [2]
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Herpes?
The signs and symptoms associated with HSV-2 are many and varied. Oral herpes caused by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) looks like cold sores on the mouth. A kiss from someone with HSV-1 who has a cold sore can give you the virus. [1]
The first outbreak of the virus usually occurs within two weeks after the virus is transmitted, and the sores typically heal within two to four weeks. [2] There may be a second crop of sores and flu-like symptoms (fever, body aches, and swollen glands) however most individuals with HSV-2 infection never have sores. People diagnosed with genital herpes can expect to have several (typically four or five) outbreaks within the first year. Over time these recurrences usually decrease in frequency. [2]
Diagnosis of Herpes
A doctor can diagnose herpes via visual inspection if the outbreak is typical, and by taking a sample from the sore(s) and testing it for the virus. Infections can be diagnosed between outbreaks using a blood test, although the results are not always clear. [2]
Treatment of Herpes
There is no treatment that can cure herpes, but antiviral medications can shorten and prevent outbreaks during the period of time the person takes the medication. In addition, daily suppressive therapy for symptomatic herpes can reduce transmission to partners. [1]
Prevention of Herpes
The surest way to avoid transmission of sexually transmitted diseases, including genital herpes, is to abstain from sexual contact. Persons with herpes should abstain from sexual activity with uninfected partners, especially when lesions or other symptoms of herpes are present. Even if a person does not have any symptoms they can still infect sexual partners and they should use condoms to reduce the risk. [1]
References
- http://www.webmd.com/genital-herpes/guide/genital-herpes-overview-facts
- STD facts- Genital herpes. http://www.cdc.gov/std/herpes/stdfact-herpes.htm
- Corey L, Wald A. Genital herpes. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Mardh P et al (eds). Sexually Transmitted Disease, 3rd Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1999, p. 285-312


